DCSE Self-Study Training MaterialsRAID Theory |
|
||||||||
RAID 50
RAID 50 was also never sanctioned by the RAID Advisory Board (RAB). It is common to combine the basic RAID levels to produce a configuration that is more appropriate to a system's specific I/O requirements. Although there has yet to be a standard initiated this is how the PERC Controllers handle RAID 10 and RAID 50.
RAID 50 provides the features of both RAID 0 and RAID 5. RAID 50 includes both parity and disk striping across multiple drives. RAID 50 is best implemented on two RAID 5 disk arrays with data striped across both disk arrays. RAID 50 breaks up data into smaller blocks, and then stripes the blocks of data to each RAID 5 disk set. RAID 5 breaks up data into smaller blocks, calculates parity by performing an exclusive-or on the blocks, and then writes the blocks of data and parity to each drive in the array. The Size of each block is determined by the stripe size parameter, which is set during the creation of the RAID set.
RAID 50 can sustain one to eight drive failures while maintaining data integrity if each failed disk is in a different RAID 5 array.
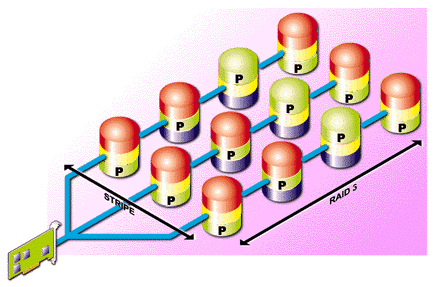
RAID 50: Four Level 5 RAIDs striped together as a RAID 0.